本系列文章配套代码获取有以下两种途径:
-
通过百度网盘获取:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1XuxKa9_G00NznvSK0cr5qw?pwd=mnsj提取码:mnsj
-
前往GitHub获取:
https://github.com/returu/PyTorch可以说,损失函数在神经网络训练过程中起着导向作用。它告诉神经网络在每次迭代中应该如何调整其内部参数(如权重和偏置),以最小化预测误差。通过反复调整参数来减少损失函数的值,神经网络能够逐渐学习到从输入数据到期望输出的正确映射。
均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE)和交叉熵损失(Cross-Entropy Loss)是两种常用的损失函数,有时可能也会使用到负对数似然损失(Negative Log Likelihood Loss,NLLLoss),它们在不同的机器学习任务中发挥着关键作用。
均方误差(MSE):
均方误差(Mean Squared Error,MSE)损失函数是一种常用的回归损失函数,用于衡量模型预测值与真实值之间的差异。其具体计算方式是将每个样本的预测值与真实值之差进行平方,然后对所有样本取平均。
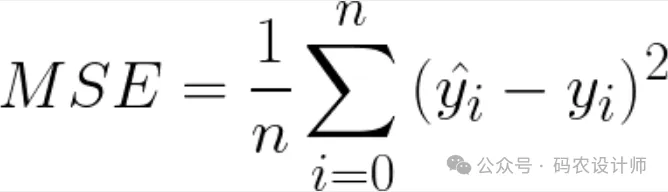

均方误差计算简单,易于理解,通常用于回归任务,特别是当目标变量是连续的时。例如,在房价预测、温度预测等任务。
-
基于Python实现:
import numpy as np
# 定义函数
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):
"""
计算均方误差MSE
:param y_true: 真实值数组
:param y_pred: 预测值数组
:return: 均方误差
"""
return np.mean((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
# 生成y_true(真实值)示例数据
input = np.random.randn(3, 5)
# 生成y_pred(预测值)示例数据
target = np.random.randn(3, 5)
# 计算MSE
mse = mean_squared_error(input , target)
print(f"Mean Squared Error (MSE): {mse}")
-
基于PyTorch实现:
在PyTorch中,可以使用torch.nn模块中的MSELoss类来实现均方误差(MSE)。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 转为tensor
input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(input)
target_tensor = torch.from_numpy(target)
# 使用torch.nn模块中的MSELoss类来实现均方误差(MSE)
loss = nn.MSELoss()
# 计算MSE
output = loss(input_tensor, target_tensor)
print(f"Mean Squared Error (MSE): {output}")
-
输入input:通常是模型的预测结果,需要先经过log_softmax处理,将其转换为概率分布的形式,并取对数。 -
确定目标类别class:这是真实的类别标签。 -
计算损失:根据公式loss(input, class) = -input(class)计算损失值。具体来说,就是取input中对应class的元素,并取其负值作为损失。
-
基于Python实现:
使用NumPy来实现NLLLoss时,需要注意的是,input在输入NLLLoss之前,需要对其进行log_softmax处理。
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x,axis=1, keepdims=True))
return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
# 生成y_true(真实值)示例数据
input = np.random.randn(3, 5)
input = np.log(softmax(input))
# 生成y_pred(预测值)示例数据
target = np.random.randint(0,5,size=(3))
# 定义函数
def nll_loss(input, targets):
# 计算每个样本的损失
losses = -input[range(input.shape[0]), target]
# 返回平均损失
return np.mean(losses)
# 计算NLLLoss
nll_loss = nll_loss(input , target)
print(f"Negative Log Likelihood Loss (NLLLoss): {nll_loss}")
-
基于PyTorch实现:
在PyTorch中,可以使用torch.nn模块中的NLLLoss类来实现均方误差(NLLLoss)。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 转为tensor
input = torch.from_numpy(input)
target = torch.from_numpy(target).to(dtype=torch.long)
# 创建NLLLoss损失函数对象
nll_loss = nn.NLLLoss()
# 计算NLLLoss
loss = nll_loss(input, target)
print(f"Negative Log Likelihood Loss (NLLLoss): {loss}")
交叉熵损失(Cross Entropy Loss):
交叉熵损失(Cross Entropy Loss)是一种常用的损失函数,主要用于分类问题。它基于信息论中的交叉熵概念,用于衡量模型的预测结果与真实标签之间的差异。
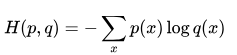
-
二分类问题:

-
多分类问题:

(1)Example of target with class indices
-
基于Python实现:
import numpy as np
# 生成y_true(真实值)示例数据
input = np.random.randn(3, 5)
# 生成y_pred(预测值)示例数据
target = np.random.randint(0,5,size=(3))
def softmax(x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x,axis=1, keepdims=True))
return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
# 定义函数
def cross_entropy_loss(input , target):
#计算输入softmax,此时可以看到每一行加到一起结果都是1
soft_output=softmax(input)
#在softmax的基础上取log
log_output = -np.log(soft_output)
# 根据真实标签选取对应的网络输出概率(取log后的),再求平均值
res = np.mean(log_output[range(len(log_output)) , target])
return res
# 计算Cross Entropy Loss
cross_entropy_loss = cross_entropy_loss(input , target)
print(f"Cross Entropy Loss: {cross_entropy_loss}")
-
基于PyTorch实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 转为tensor
input = torch.from_numpy(input)
target = torch.from_numpy(target).to(dtype=torch.long)
# 创建CrossEntropyLoss损失函数对象
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 计算Cross Entropy Loss
loss = loss(input, target)
print(f"Cross Entropy Loss: {loss}")
类概率表示每个样本属于各个类别的概率分布。在多分类问题中,对于每个样本,我们会为每个类别分配一个概率值,这些概率值的总和为1。这通常用于表示模型对于样本属于每个类别的置信度。在这种情况下,模型的任务是预测出与真实概率分布尽可能接近的输出概率分布。
-
基于Python实现:
import numpy as np
# 生成y_true(真实值)示例数据
input = np.random.randn(3, 5)
def softmax(x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x,axis=1, keepdims=True))
return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
# 生成y_pred(预测值)示例数据
target = np.random.randn(3, 5)
target = softmax(target)
# 定义函数
def cross_entropy_loss(input, target):
#计算输入softmax,此时可以看到每一行加到一起结果都是1
soft_output=softmax(input)
#在softmax的基础上取log
log_output = -np.log(soft_output)
return np.mean(np.sum(target * log_output, 1))
# 计算Cross Entropy Loss
cross_entropy_loss = cross_entropy_loss(input , target)
print(f"Cross Entropy Loss: {cross_entropy_loss}")
-
基于PyTorch实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 转为tensor
input = torch.from_numpy(input)
target = torch.from_numpy(target)
# 创建CrossEntropyLoss损失函数对象
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 计算Cross Entropy Loss
loss = loss(input, target)
print(f"Cross Entropy Loss: {loss}")
通过上述示例代码,可以看出,Pytorch中,CrossEntropyLoss()不单是做了交叉熵,而且在里面还加入了log和softmax,即:
Cross Entropy Loss=softmax+log+NLLLoss。
更多内容可以前往官网查看:
https://pytorch.org/


本篇文章来源于微信公众号: 码农设计师
