class Polygon(shell[, holes=None])
The Polygon constructor takes two positional parameters. The first is an ordered sequence of (x, y[, z]) point tuples and is treated exactly as in the LinearRing case. The second is an optional unordered sequence of ring-like sequences specifying the interior boundaries or “holes” of the feature.
Polygon构造函数需要两个位置参数。第一个位置参数是一个(x, y[, z])点元祖的有序序列,与LinearRing的情况完全相同。第二个位置参数是一个可选的无序的环状序列,用于指定几何要素的内部”洞”的边界 。
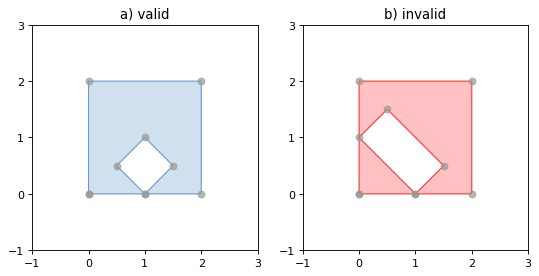
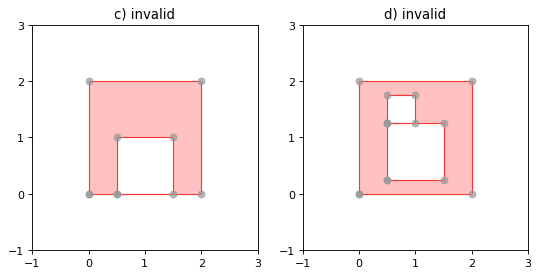
Rings of a valid Polygon may not cross each other, but may touch at a single point only. Again, Shapely will not prevent the creation of invalid features, but exceptions will be raised when they are operated on.
一个有效的多边形的环不能相互交叉,而只能在一个点上接触。同样,Shapely不会阻止无效要素的创建,但在对其进行操作时可能会出现异常。
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
A Polygon has non-zero area and non-zero length.
一个多边形具有非零的面积和非零的长度。
>>> from shapely import Polygon
>>> polygon = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 1), (1, 0)])
>>> polygon.area
0.5
>>> polygon.length
3.414213562373095Its x-y bounding box is a (minx, miny, maxx, maxy) tuple.
它的边界是一个元组(minx, miny, maxx, maxy)。
>>> polygon.bounds
(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)Component rings are accessed via exterior and interiors properties.
内环和外环可以通过exterior和interiors属性进行访问。
>>> list(polygon.exterior.coords)
[(0.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0), (1.0, 0.0), (0.0, 0.0)]
>>> list(polygon.interiors)
[]The Polygon constructor also accepts instances of LineString and LinearRing.
Polygon构造函数也接受LineString和LinearRing实例。
>>> coords = [(0, 0), (1, 1), (1, 0)]
>>> r = LinearRing(coords)
>>> s = Polygon(r)
>>> s.area
0.5
>>> t = Polygon(s.buffer(1.0).exterior, [r])
>>> t.area
6.5507620529190325Rectangular polygons occur commonly, and can be conveniently constructed using the shapely.geometry.box() function.
矩形多边形经常出现,可以使用shapely.geometry.box()函数方便地构建。
- shapely.geometry.box(minx, miny, maxx, maxy, ccw=True)
Makes a rectangular polygon from the provided bounding box values, with counter-clockwise order by default.
根据提供的边界框值生成一个矩形的多边形,默认为逆时针顺序。
New in version 1.2.9.
For example:
>>> from shapely import box
>>> b = box(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> b
<POLYGON ((1 0, 1 1, 0 1, 0 0, 1 0))>
>>> list(b.exterior.coords)
[(1.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0), (0.0, 1.0), (0.0, 0.0), (1.0, 0.0)]This is the first appearance of an explicit polygon handedness in Shapely.
To obtain a polygon with a known orientation, use shapely.geometry.polygon.orient():
为了获得一个已知方向的多边形, 可以使用shapely.geometry.polygon.orient():
Returns a properly oriented copy of the given polygon. The signed area of the result will have the given sign. A sign of 1.0 means that the coordinates of the product’s exterior ring will be oriented counter-clockwise and the interior rings (holes) will be oriented clockwise.
返回给定多边形正确方向的副本。结果中带符号区域将具有给定的符号。sign为1.0意味着矩形外部环的坐标将是逆时针方向的,内部环(孔)将是顺时针方向的。
New in version 1.2.10.
